MODERN PORTFOLIO THEORY
Harry Markowitz received the Nobel Prize for Economics in 1990, along with William Sharp and Merton Miller, for their contributions to financial economics and investment field. Modern Portfolio Theory, has been developed by Markowitz in 1950s which illustrates how investment risks in the financial market can have a maximized return.
His first article on “Portfolio Selection,” which explains his theory in early 1952. Markowitz utilized mathemetics and computer methods applied to realistic problems, such as uncertainty in business decisions. In 1989, he was awarded the Von Neumann Prize in Operations Research Theory by the Operations Research Society of America and The Institute of Management Sciences.
Modern portfolio theory (MPT) is a theory of investment that attempts to maximize portfolio expected return for a given amount of portfolio risk, and minimizing risk for a given level of expected return, by carefully choosing the proportions of various assets thats available in the market. His idea normally proposed inventors should select portfolios as their investment strategy intead of invest in individual securities/stock.
Efficient Frontier: Refers to the optimal portfolios plotted along the curve with the highest expected return possible for the given amount of risk. (the set of all portfolios that will give the highest expected return for each given level of risk.) These concepts of efficiency were essential to the development of the Capital Asset Pricing Model to find the Security Market Line.
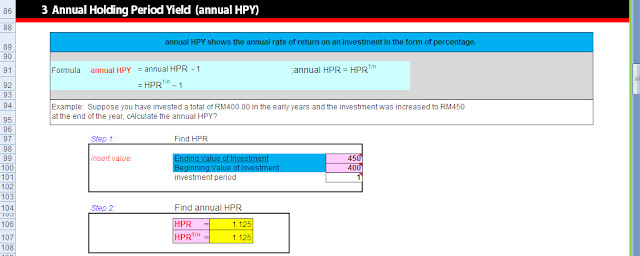
Figure 1
 Figure 1
Figure 1 As shown in this graph, the best investment option for investor to make is when the efficient frontier touch the market line. Any combination of investments below the market line or below efficient frontier may give higher risk, since the instruments are 'over valued'. Therefor, portfolio's below the curve are not efficient, because at the same risk level, investor could achieve a greater return, e.g. invest in Risk-Free Asset.
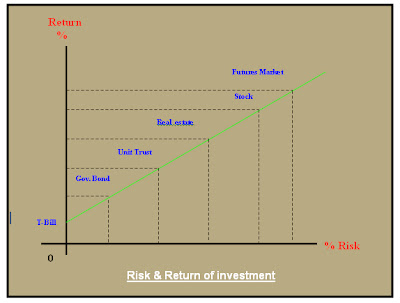
Figure 2:
Figure 2: Figure shown the relationship between risks and returns for every portfolio combinations. The higher the returns, will expose investors to higher levels of risk.
As a conclusion, portfolio will give advantages to the investors to eliminate some risks in their investment, but they have to make sure that the combination of portfolio is well diversified, meaning to say, investors should invest in various industries and avoid the over-valued assets as shown in the above Figure.